20. Superior MaskRCNN Interface Guidance
20.1. MaskRCNN Basic
A two-stage MaskRCNN is comprised of two parts:
3 weighted blocks: includes
backbone.ptand 2bbox/maskintermediate layers (namelytorch_bbox/mask.pt).5 dynamic non-weight blocks: includes
RPN head,bbox pooler,bbox head,mask poolerandmask head.
Thus, the MaskRCNN is expressed by the following procedures:
bbox detector:
backbone.pt=>RPN head=>bbox pooler=>torch_bbox.pt=>bbox head.mask detector:
backbone.pt=>RPN head=>mask pooler=>torch_mask.pt=>mask head.
20.1.1. Fast Block Segmentation Methods
Due to compatibility issues between MaskRCNN and the original framework, users may be unable to trace each part. This chapter uses the mask head as an example of a part that cannot be traced.
The segmentation points for two types of MaskRCNN blocks,are precisely the first entry points to the first layer of next weight blocks, when searching the MaskRCNN graph topologically.
20.2. Superior MaskRCNN
As the fine-grained operation-based deployment towards cloning MaskRCNN encounters challenges with high complexity in dynamic ir transformation, the following superior MaskRCNN solution is proposed:
Coarse-grained:
Built-In MaskRCNN-Exclusive Backend: now mlir-backend directly supports dynamic non-weight blocks, currently including the
RPN head,box head,bbox pooler, and maskpooler. Thus most heavy workloads related to frontend inference graph parser and optimization are saved. This allows for the avoidance of numerous dynamic shape inference or variant Op support.Model Reconstruction: users only need 4 structural information to reconstruct the complete MaskRCNN:
io_map: describes the blocks’ interfaces and always maintains the same topology as MaskRCNN. Defined as
{(destination_block_id, operand_id):(source_block_id, operand_id)}.Backbone: from top to RPN typically, split from the original MaskRCNN in advance.
Weighted blocks:
bbox/maskintermediate layers, split from the original MaskRCNN in advance.config.yaml: a yaml file to store hyper-parameters, provided in advance.
20.3. Quick Start
Before dive into new MaskRCNN features, please first explore the new yaml file and new unit tests for MaskRCNN.
20.3.1. Prepare Your Yaml
A default yaml is prepared at regression/dataset/MaskRCNN/CONFIG_MaskRCNN.yaml, whose struct is:
Compile Parameters for model_transform: structural infomations to reconstruct MaskRCNN.
- io_map: defined as {(destination_block_id, operand_id):(source_block_id, operand_id)}; here -1 represents the complete model’s top inputs, -2 represents the complete model’s top outputs, and 0, 1, 2… represents the id of MaskRCNN blocks.
For example, {(0,0):(-1,0),(1,0):(0,0),(-2,0):(1,0)} means block[0]’s input[0] comes from input[0] of the complete model, block[1]’s input[0] comes from block[0]’s output[0], and output[0] of the complete model comes from block[1]’s output[0].
maskrcnn_output_num: number of final output operands for the complete MaskRCNN.
maskrcnn_structure: the list describing the order of MaskRCNN blocks. 1 means a torch.pt model, while 0 means PPLOp. For example, [1, 0, 1] means the 1st launches a torch model, the 2nd launches a PPLOp, and the 3rd launches another torch model.
maskrcnn_ppl_op: names of MaskRCNN operands implemented by PPL at the backend.
numPPLOp_InWithoutWeight_MaskRCNN: number of input operands for each PPLOp; remember not to count weight operands.
Hyper-parameters for MaskRCNN: nececssary MaskRCNN parameters, decided by the original MaskRCNN framework.
20.3.2. Block Unit Test
Use --case to test 4 dynamic non-weight blocks: RPN head, bbox pooler, bbox head, mask pooler.
More guidance will be found at python/test/test_MaskRCNN.py.
$ test_MaskRCNN.py --case MaskRCNN_Utest_RPNGetBboxes --debug
20.4. New Frontend Interface API
20.4.1. [Step 1] Run model_transform
Used to convert MaskRCNN into MLIR files.
Skip Inference: please be aware that no input/reference data
.npzfiles are needed at this step, but aconfig.yamlis required in advance.Skip Preprocess: please note that in this step, no preprocessing is applied by default.
New Enable Flag: please remeber
enable_maskrcnn.
$ model_transform.py \
--model_def backbone.pt \
--model_extern torch_bbox.pt,torch_mask.pt \
--model_name MaskRCNN \
--input_shapes [[1,3,800,1216],[1,1,4741,4],[1,1,20000,4],[1,1,20000,4],[1,1,100,4]] \
--mlir MaskRCNN.mlir \
--enable_maskrcnn \
--path_yaml regression/dataset/MaskRCNN/CONFIG_MaskRCNN.yaml
20.4.2. [Step 2] Generate Input Data
20.4.2.1. MaskRCNN Input Format
The MaskRCNN implemented by the proposed method requires 5 inputs:
preprocessed image: image after preprocessing.
max_shape_RPN/max_shape_GetBboxB: if input image is resized to shape
S1and original shape isS0,then max shape isint(S0 * S1 / S0), and expanded to a constant weight tensor.scale_factor_GetBboxB/scale_factor_MaskPooler: if input image is resized to shape
S1and original shape isS0,then scale factor isfloat(S1 / S0), and expanded to a constant weight tensor.
20.4.2.2. Input Formats Reorganizing Tools
A tool is offered at tpu-mlir/python/tools/tool_maskrcnn.py to assist you in generating data satisfied with the above requirements.
Skip Preprocess: input image shoud be after preprocess, as preprocess procedure for MaskRCNN is usually complex and relies on specific functions from original framework.
Besides path_yaml, 3 more parameters need to be specifc:
path_input_image: image after preprocessing, saved as npz.
basic_max_shape_inverse: the height and width after preprocessing.
basic_scalar_factor: precisely the above
float(S1 / S0),basic_max_shape_inversedivide orginal shape reordered inheight, width.
The result data will be stored at same path of path_input_image, but suffixed by SuperiorMaskRCNNInputPreprocessed.
Please explore tool_maskrcnn.py for more guidance.
$ tool_maskrcnn.py \
--path_yaml ./regression/dataset/MaskRCNN/CONFIG_MaskRCNN.yaml \
--path_input_image ./regression/dataset/MaskRCNN/Superior_IMG_BackBone.npz \
--basic_max_shape_inverse 1216,800 \
--basic_scalar_factor 1.8734375,1.8735363 \
--debug
20.4.3. [Step 3] Run model_deploy
Inference Skip: quant compare and simulation compare are skipped here.
Mandatory Parameters:
--quantizemode is forced to beF32and--processoris forced to beBM1684X.New Enable Flag: please remeber
enable_maskrcnn.
$ model_deploy.py \
--mlir MaskRCNN.mlir \
--quantize F32 \
--processor BM1684X \
--model MaskRCNN.bmodel \
--debug \
--enable_maskrcnn
20.5. IO_MAP Guidance
Manually generate io_map in two steps:
Well-SuppliedDefinition of Block Interfaces: precisely collect input and output operand shapes, and block connection patterns.
Create Corresponding io_map: it should precisely and uniquely reconstruct the complete MaskRCNN.
20.5.1. [Step-1] Describe Block Interface
A complete MaskRCNN is truncated into multiple blocks as discussed above.
Please describe following information for each block:
Input: input operands or constant weights
shapes: in 4-dims format.
dtypes: only support fp32 or int32.
connections: the corresponding output of the upper block which each input is sourced from and specifying which operand it originates from.
Note that -1 represents the inputs of the complete MaskRCNN, while -2 the outputs of the complete model. And bs represents batch_size.
[-1] Top_In
Input Number |
Name |
Shape |
Dtype |
|---|---|---|---|
Input 0) |
‘img.1’ |
[1,3,800,1216] |
|
Input 1) |
‘max_shape_RPN’ |
[bs,1,max_filter_num,4] |
int32 |
Input 2) |
‘max_shape_GetBboxB’ |
[1,bs*20000,1,4] |
int32 |
Input 3) |
‘scale_factor_GetBboxB’ |
[1, bs,20000,4] |
FP32 |
Input 4) |
‘scale_factor_MaskPooler’ |
[bs,1,roi_slice,4] |
FP32 |
[Torch] SubBlock-0: BackBone.pt
IO-Type |
Name |
Shape |
Dtype |
Connection Info[From] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Input 0) |
‘img.1’ |
[1,3,800,1216] |
FP32 |
[TOP_IN]Input-0 |
Output 0) |
‘11’ |
[1,256,200,304] |
FP32 |
|
Output 1) |
‘12’ |
[1,256,100,152] |
FP32 |
|
Output 2) |
‘13’ |
[1,256,50,76] |
FP32 |
|
Output 3) |
‘16’ |
[1,256,25,38] |
FP32 |
|
Output 4) |
‘15’ |
[1,256,13,19] |
FP32 |
|
Output 5) |
‘18’ |
[1,3,200,304] |
FP32 |
|
Output 6) |
‘19’ |
[1,3,100,152] |
FP32 |
|
Output 7) |
‘20’ |
[1,3,50,76] |
FP32 |
|
Output 8) |
‘21’ |
[1,3,25,38] |
FP32 |
|
Output 9) |
‘22’ |
[1,3,13,19] |
FP32 |
|
Output 10) |
‘23’ |
[1,12,200,304] |
FP32 |
|
Output 11) |
‘24’ |
[1,12,100,152] |
FP32 |
|
Output 12) |
‘25’ |
[1,12,50,76] |
FP32 |
|
Output 13) |
‘26’ |
[1,12,25,38] |
FP32 |
|
Output 14) |
‘27’ |
[1,12,13,19] |
FP32 |
[PPL] SubBlock-1: ppl::RPN_get_bboxes
IO-Type |
Name |
Shape |
Connection Info[From] |
|---|---|---|---|
Output |
0 result_list |
[bs,1,max_per_img,num_levels] |
|
Input |
1 cls_scores_0 |
[bs,3,200,304] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 5) |
Input |
2 cls_scores_1 |
[bs,3,100,152] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 6) |
Input |
3 cls_scores_2 |
[bs,3,50,76] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 7) |
Input |
4 cls_scores_3 |
[bs,3,25,38] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 8) |
Input |
5 cls_scores_4 |
[bs,3,13,19] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 9) |
Input |
6 bbox_preds_0 |
[bs,12,200,304] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 10) |
Input |
7 bbox_preds_1 |
[bs,12,100,152] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 11) |
Input |
8 bbox_preds_2 |
[bs,12,50,76] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 12) |
Input |
9 bbox_preds_3 |
[bs,12,25,38] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 13) |
Input |
10 bbox_preds_4 |
[bs,12,13,19] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 14) |
Input |
11 max_shape |
[bs,1,max_filter_num,5] |
[TOP_IN]Input-1 |
Input |
12 mlvl_anchors_0 |
[bs,1,3*200*304,5] |
[mlir][Weight] |
Input |
13 mlvl_anchors_1 |
[bs,1,3*100*152,5] |
[mlir][Weight] |
Input |
14 mlvl_anchors_2 |
[bs,1,3*50*76,5] |
[mlir][Weight] |
Input |
15 mlvl_anchors_3 |
[bs,1,3*25*38,5] |
[mlir][Weight] |
Input |
16 mlvl_anchors_4 |
[bs,1,3*13*19,5] |
[mlir][Weight] |
[PPL] SubBlock-2: ppl::Bbox_Pooler
IO-Type |
Name |
Shape |
Connection Info[From] |
|---|---|---|---|
Output |
0 result_res |
[bs*250,256,PH,PW] |
|
Output |
1 result_rois |
[bs,max_per_img,1,roi_len] |
|
Input |
2 feat0 |
{bs,256,H,W} |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 0) |
Input |
3 feat1 |
[bs,256,H/2,W/2] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 1) |
Input |
4 feat2 |
[bs,256,H/4,W/4] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 2) |
Input |
5 feat3 |
[bs,256,H/8,W/8] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 3) |
Input |
6 rois_multi_batch |
[bs,roi_slice,1,roi_len] |
[PPL][SubBlock-1]result_list |
[Torch] SubBlock-3: torch_bbox.pt
Batch |
IO-Type |
Name |
Shape |
Dtype |
Connection Info[From] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Batch-1 |
Input |
0 |
[250,256,7,7] |
FP32 |
[PPL][SubBlock-2]result_res |
Output |
0 |
[250,81] |
FP32 |
||
Output |
1 |
[250,320] |
FP32 |
[PPL] SubBlock-4: ppl::get_bboxes_B
Batch |
IO-Type |
Name |
Shape |
Connection Info[From] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Batch 1 |
Output |
result_det_bboxes |
[bs,1,100,5] |
|
Output |
result_det_labels |
[bs,1,100,1] |
||
Input |
rois |
[1,bs*250,1,5] |
[PPL][SubBlock-2]1-result_rois |
|
Input |
bbox_pred |
[1,bs*250,1,320] |
[Torch][SubBlock-3]Output 1 |
|
Input |
cls_score |
[1,bs*250,1,81] |
[Torch][SubBlock-3]Output 0 |
|
Input |
max_val |
[1,bs*20000,1,4] |
[TOP_IN]Input-2 |
|
Input |
scale_factor |
[1,bs,20000,4] |
[TOP_IN]Input-3 |
[PPL] SubBlock-5: ppl::Mask_Pooler
IO-Type |
Index |
Name |
Shape |
Connection Info[From] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Output |
0 |
result_res |
[roi_num,C,PH,PW] |
|
Input |
1 |
x0 |
[bs,256,H,W] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 0 |
Input |
2 |
x1 |
[bs,C,H/2,W/2] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 1 |
Input |
3 |
x2 |
[bs,C,H/4,W/4] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 2 |
Input |
4 |
x3 |
[bs,C,H/8,W/8] |
[Torch][SubBlock-0]Output 3 |
Input |
5 |
det_bboxes_multi_batch |
[bs,1,roi_slice,roi_len] |
[PPL][SubBlock-4]0-result_det_bboxes |
Input |
6 |
det_labels_multi_batch |
[bs,1,roi_slice,1] |
[PPL][SubBlock-4]1-result_det_labels |
Input |
7 |
scale_factor |
[bs,1,roi_slice,4] |
[TOP_IN]Input-4 |
[Torch] SubBlock-6: torch_mask.pt
Batch |
IO-Type |
Index |
Name |
Shape |
Dtype |
Connection Info[From] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Batch-1 |
Input |
0 |
input.2 |
[100,256,14,14] |
FP32 |
[PPL][SubBlock-5]0-result_res |
Output |
0 |
75 |
[100,80,28,28] |
FP32 |
||
Batch-4 |
Input |
0 |
input.2 |
[400,256,14,14] |
FP32 |
|
Output |
0 |
75 |
[400,80,28,28] |
FP32 |
[-2] TSubBlock-7: TOP_OUT
IO-Type |
Index |
Shape |
Dtype |
Connection Info[From] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Output |
0 |
[bs,1,100,5] |
FP32 |
[PPL][SubBlock-5]0-result_det_bboxes |
Output |
1 |
[bs,1,100,1] |
FP32 |
[PPL][SubBlock-5]1-result_det_labels |
Output |
2 |
[100,80,28,28] |
FP32 |
[Torch][SubBlock-6] |
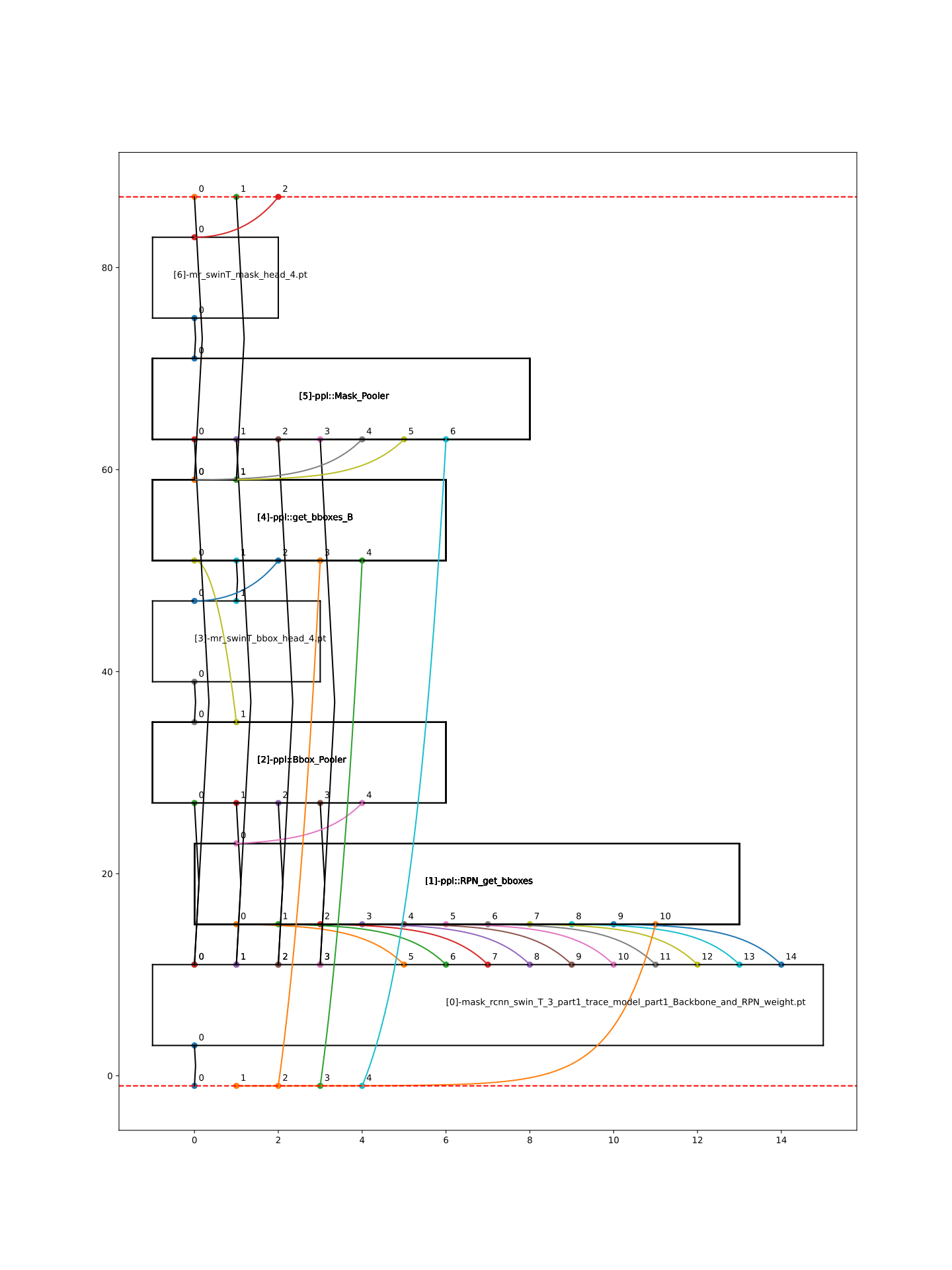
20.5.2. [Step-2] Describe IO_MAP
Reorganize above block interfaces in the following format:
Block Name:Name and serial index of one block.
Inputs: the corresponding output of the upper block from which each input is sourced and specifying which operand it originates from.
Connections: record total amounts of input operands
Mapping: use the definition,
(destination_block_index,operand_index):(source_block_index:operand_index)
Note that -1 represents the inputs of the complete MaskRCNN, while -2 the outputs of the complete model.
[0]TORCH_0-rpn
Inputs:
← [-1]TOP_IN[0]
Connections: 1
Mapping:
(0,0):(-1,0)
[1]PPL-RPNGetBboxes
Inputs:
← [0]TORCH_0-rpn[5:15]
← [-1]TOP_IN[1]
Connections: 10
Mapping:
(1,0):(0,5)
(1,1):(0,6)
(1,2):(0,7)
(1,3):(0,8)
(1,4):(0,9)
(1,5):(0,10)
(1,6):(0,11)
(1,7):(0,12)
(1,8):(0,13)
(1,9):(0,14)
(1,10):(-1,1)
[2]PPL-Bbox_Pooler
Inputs:
← [0]TORCH_0-rpn[0:4]
← [1]PPL-RPNGetBboxes[0]
Connections: 4 + 1
Mapping:
(2,0):(0,0)
(2,1):(0,1)
(2,2):(0,2)
(2,3):(0,3)
(2,4):(1,0)
[3]Torch-2
Inputs:
← [2]PPL-Bbox_Pooler
Connections: 1
Mapping:
(3,0):(2,0)
[4]PPL-GetBboxB
Inputs:
← [2]PPL-Bbox_Pooler[1]
← [3]Torch-2[0:2]_inverse
← [-1]TOP_IN[2:4]
Connections: 1 + 2 (inverse) + 2
Mapping:
(4,0):(2,1)
(4,1):(3,1)
(4,2):(3,0)
(4,3):(-1,2)
(4,4):(-1,3)
[5]ppl-MaskPooler
Inputs:
← [0]Torch-RPN[0:4]
← [4]PPL-GetBboxB[0:2]
← [-1]TOP_IN[4]
Connections: 4 + 2
Mapping:
(5,0):(0,0)
(5,1):(0,1)
(5,2):(0,2)
(5,3):(0,3)
(5,4):(4,0)
(5,5):(4,1)
(5,6):(-1,4)
[6]Torch-3
Inputs: ← [5]ppl-MaskPooler
Connections: 1
Mapping: (6,0):(5,0)
[-2]TOP_OUT
Inputs:
← [4]PPL-GetBboxB[0:2]
← [6]Torch-3
Connections: 2 + 11
Mapping:
(-2,0):(4,0)
(-2,1):(4,1)
(-2,2):(6,0)
20.6. Generate IO_MAP
After collecting all mapping information above, an io_map dictionary is generated:
io_map: {(0,0):(-1,0),(1,0):(0,5),(1,1):(0,6),(1,2):(0,7),(1,3):(0,8),(1,4):(0,9),(1,5):(0,10),(1,6):(0,11),(1,7):(0,12),(1,8):(0,13),(1,9):(0,14),(1,10):(-1,1),(2,0):(0,0),(2,1):(0,1),(2,2):(0,2),(2,3):(0,3),(2,4):(1,0),(3,0):(2,0),(4,0):(2,1),(4,1):(3,1),(4,2):(3,0),(4,3):(-1,2),(4,4):(-1,3),(5,0):(0,0),(5,1):(0,1),(5,2):(0,2),(5,3):(0,3),(5,4):(4,0),(5,5):(4,1),(5,6):(-1,4),(6,0):(5,0),(-2,0):(4,0),(-2,1):(4,1),(-2,2):(6,0)}
Now directly use it at model_transform, which will further dump a revised_io_map_${model_name}.svg image to assist you in visualizing the io_map.
20.7. mAP Inference
Transform and deploy such a coarse-grained MaskRCNN is not enough, to apply the mAP inference on the COCO2017 dataset, a careful intersection into the original framework is required.
Please refer to our model-zoo project for more inference details.