The TPU-MLIR compiler is capable of transforming deep learning models running on platforms such as GPUs into bmodel models that can run on arithmetic capability chips. This document provides an overview of how to use TPU-MLIR to port the stable diffusion model running on GPUs to arithmetic capability chips, along with the deployment methods involved. As stable diffusion encompasses multiple versions, we will use stable diffusion version 1.5 as an example here.
Introduction to the Stable Diffusion Model#
The stable diffusion model consists of three components: text_encoder, unet, and vae. The three readily usable models for these components are: CLIP_ViT, Latent Diffusion Models, and AutoencoderKL VAE. The model execution process is illustrated in the following figure:
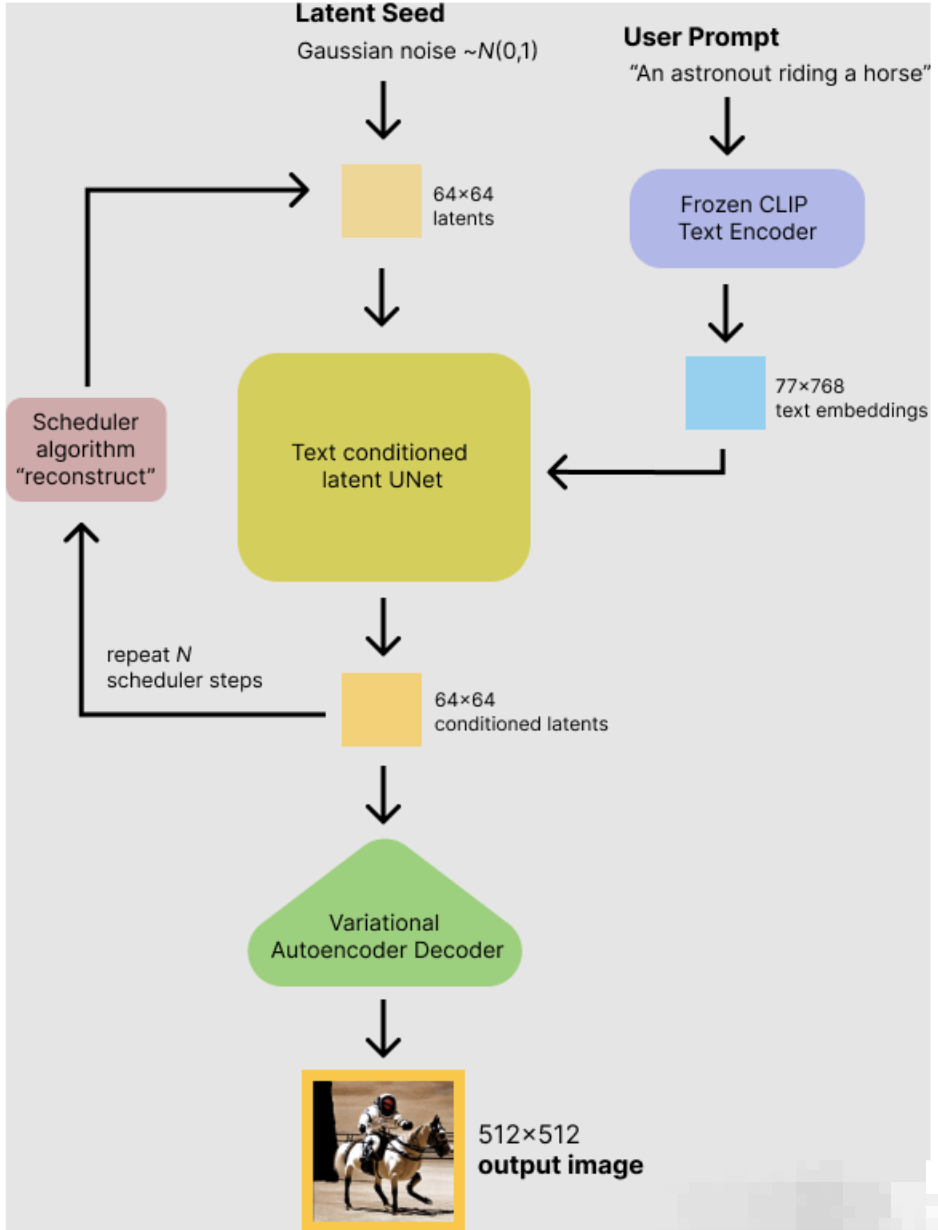
Transform stable diffusion involves transplanting each of the three model components onto the arithmetic capability processor, and then connecting these three components together to form a complete stable diffusion model.
Transform the Stable Diffusion Model#
Get the Stable Diffusion Model#
The stable diffusion model can be obtained from the hugging face model hub. The following code snippet shows how to get the stable diffusion model from the hugging face model hub:
1 | from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline |
Please refer https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5.
Transform the Text Encoder#
The text encoder is a CLIP_ViT model, which can be transformed into a onnx model, and then the onnx model can be transformed into a bmodel model.
Transform into an onnx model#
1 | def export_textencoder(pipe): |
Make a transformation script#
1 | model_transform.py --model_name encoder --input_shape [[1,77]] --model_def encoder.onnx --mlir encoder.mlir |
Run this transformation script to transform the onnx model into a bmodel model.
Transform the Unet Model#
The unet model is a Latent Diffusion Models model, which can be transformed into a pt model, and then the pt model can be transformed into a bmodel model.
Transform into a pt model#
1 | def myunet(self, latent, timestep, encoder_hidden_states): |
By constructing a fake_input with a batch of 2, and then converting the unet model into a pt model using torch.jit.trace. The batch of 2 is considered to be the negative prompt and positive prompt cases, so the model uses a batch of 2.
Make a transformation script#
1 | model_transform.py --model_name unet --input_shape [[2,4,64,64],[1],[2,77,768]] --model_def unet.pt --mlir unet.mlir |
Transform the VAE Model#
VAE is split into two parts in stable diffusion, encoder and decoder. Here we can convert the encoder and decoder into pt models, and then construct a conversion script to convert the pt models into bmodel models.
Transform VAE Encoder#
Transform into a pt model#
1 | def export_vaencoder(pipe): |
Make a transformation script#
1 | model_transform.py --model_name vae_encoder --input_shape [[1,3,512,512]] --model_def vae_encoder.pt --mlir vae_encoder.mlir |
Transform VAE Decoder#
Transform into a pt model#
1 | def export_vaedecoder(pipe): |
Make a transformation script#
1 | model_transform.py --model_name vae_decoder --input_shape [[1,4,64,64]] --model_def vae_decoder.pt --mlir vae_decoder.mlir |
Here we have completed all the model transformation, and obtained the corresponding bmodel files. Next, we need to string together the three parts of the model, deploy them, and get a complete stable diffusion.
Deploy the Stable Diffusion Model#
Make a deployment script#
Some version dependency information#
1 | diffusers==0.2.4 |
Build the runtime#
Use sail to build the runtime of the model. Please refer to https://doc.sophgo.com/sdk-docs/v23.05.01/docs_latest_release/docs/sophon-sail/docs/zh/html/安装sail. Here for better call, we create a class.
1 | import numpy as np |
Build Pipeline#
1 | import inspect |
Build Runtime Script#
1 | # -- coding: utf-8 --` |
It starts streamlit server accessible through a web browser.
